Science Class
domingo, 21 de agosto de 2011
miércoles, 27 de abril de 2011
Source of Energy
Solar cell: a device that generates an electric current from sunlight.

Biomas conversion: getting energy from plant and animal materials by changing them into high quality fuels.

Nuclear fission: The splitting of a nucleus with smaller masses.




Biomas conversion: getting energy from plant and animal materials by changing them into high quality fuels.

Nuclear fission: The splitting of a nucleus with smaller masses.
Chain reaction: a reaction that is kept going by products of the reaction.


Nuclear fusion: the meging of nuclei with smaller masses into a nucleus with a larger mass.

Hydroelecricity: the use of flowing water to generate electricity.

Thermal pollution: the excess heating of the environment.

martes, 26 de abril de 2011
Temperature, Heat, and Matter
Thermal expansion: the expansion of matter when its temperature is raised.
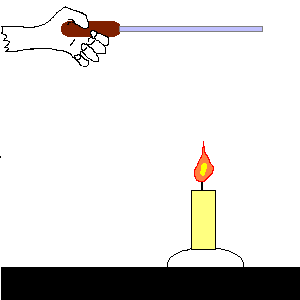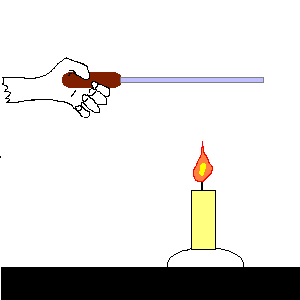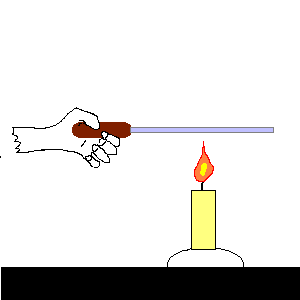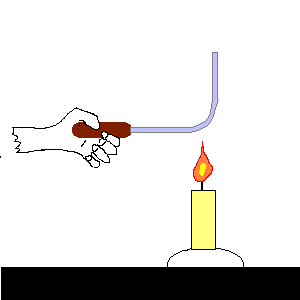
pressure: the force on each unit of area of a surface.

melting: the change of a solid into a liquid.

vaporization: the change of a liquid to a gas as molecules break free from each other.

condensation: the change of a gas into a liquid as molecules attract each other.
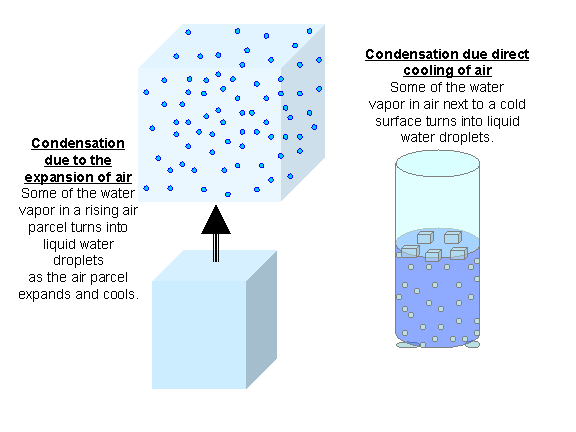
freezing: the change of liquid into a gas.

boiling: the formation of bubbles of vapor that escape from a liquid that is being heated.
-338656.jpg)
evaporation: the vaporization of molecules from the surface of a liquid.


pressure: the force on each unit of area of a surface.

melting: the change of a solid into a liquid.

vaporization: the change of a liquid to a gas as molecules break free from each other.

condensation: the change of a gas into a liquid as molecules attract each other.

freezing: the change of liquid into a gas.

boiling: the formation of bubbles of vapor that escape from a liquid that is being heated.
-338656.jpg)
evaporation: the vaporization of molecules from the surface of a liquid.

lunes, 11 de abril de 2011
SOUND
Pitch
This is how high or low a sound seems. A bird makes a high pitch. A lion makes a low pitch.
 |
Sounds also are different in how loud and how soft they are.
The more energy the sound wave has the louder the sound seems.
 |  |
 You can hear loud and soft sounds.We can do noise by example:play a drum,scream.
You can hear loud and soft sounds.We can do noise by example:play a drum,scream.

see more in http://www.mediacollege.com/audio/01/sound-waves.html
put START and you will see the saound waves...LEARN MORE!
Temperature and Heat
Kinetic energy:the energy of a moving object.
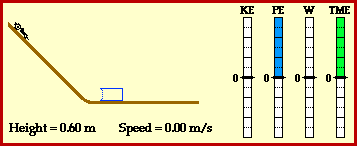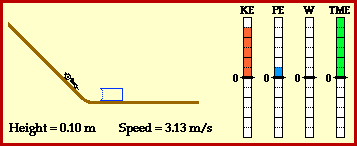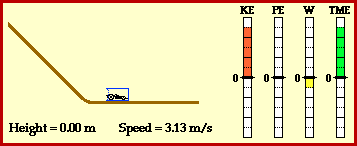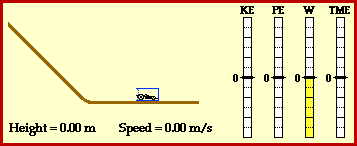
potential energy: energy stored in an object or material.
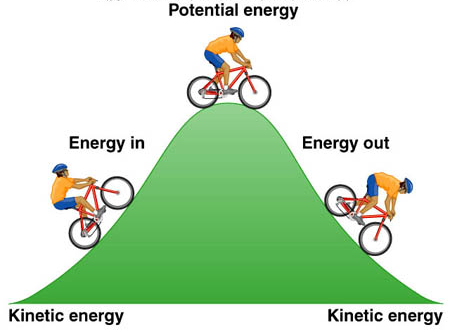
temperature: the average kinetic energy of the molecules in a material.

heat: energy that flows between objects that have different temperatures.

radiation: the transfer of energy by electromagnetic waves.
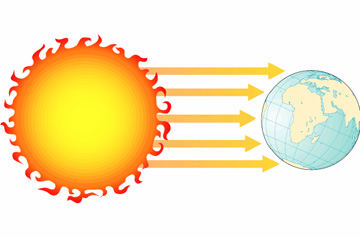
conduction: the transfer of energy by direct contact of molecules.

convection: the transfer of energy by the flow of a liquid or gas.

insulation: prevents heat from flowing in or out of a material.

potential energy: energy stored in an object or material.

temperature: the average kinetic energy of the molecules in a material.

heat: energy that flows between objects that have different temperatures.

radiation: the transfer of energy by electromagnetic waves.

conduction: the transfer of energy by direct contact of molecules.

convection: the transfer of energy by the flow of a liquid or gas.

insulation: prevents heat from flowing in or out of a material.

sábado, 9 de abril de 2011
Chemical Changes
Compound: A chemical combination of two or more elements.

Chemical bond: A link that atoms or electrically charged particles can form with each other.

Chemical Formula: A way of using letters and numbers to show how much of each element is in a substance.

ion: An elecrocally charged particle with unequal numbers of protons and electrons.

Molecule: A group of bonded atoms that acts like a single particle.

Chemical Property: A way of describing how a substance changes chemically with other substance.

Exothermic: A reaction that gives off heat.

Endothermic: A reaction that absorbs heat.


Chemical bond: A link that atoms or electrically charged particles can form with each other.

Chemical Formula: A way of using letters and numbers to show how much of each element is in a substance.

ion: An elecrocally charged particle with unequal numbers of protons and electrons.

Molecule: A group of bonded atoms that acts like a single particle.

Chemical Property: A way of describing how a substance changes chemically with other substance.

Exothermic: A reaction that gives off heat.

Endothermic: A reaction that absorbs heat.
jueves, 17 de marzo de 2011
Elements and Atoms
Element: a substance that cannot be broken down any further into anything simpler.

Atom: The smallest particle of an element that has the same chemical properties as the element.

Nucleus: An atom's dense center, where most of its mass is.
Electron: a negatively charged particle that moves around an atom's nucleus.

Proton: a positively charged particle inside an atom's nucleus.

Neutron: a particle with no charge inside an atom's nucleus.

Atomic number: the number of protons in an atom.

Metal: any group of elements that conduct heat and electricity, is shiny and bendable.


Atom: The smallest particle of an element that has the same chemical properties as the element.

Nucleus: An atom's dense center, where most of its mass is.

Electron: a negatively charged particle that moves around an atom's nucleus.

Proton: a positively charged particle inside an atom's nucleus.

Neutron: a particle with no charge inside an atom's nucleus.

Atomic number: the number of protons in an atom.

Metal: any group of elements that conduct heat and electricity, is shiny and bendable.

Suscribirse a:
Comentarios (Atom)

